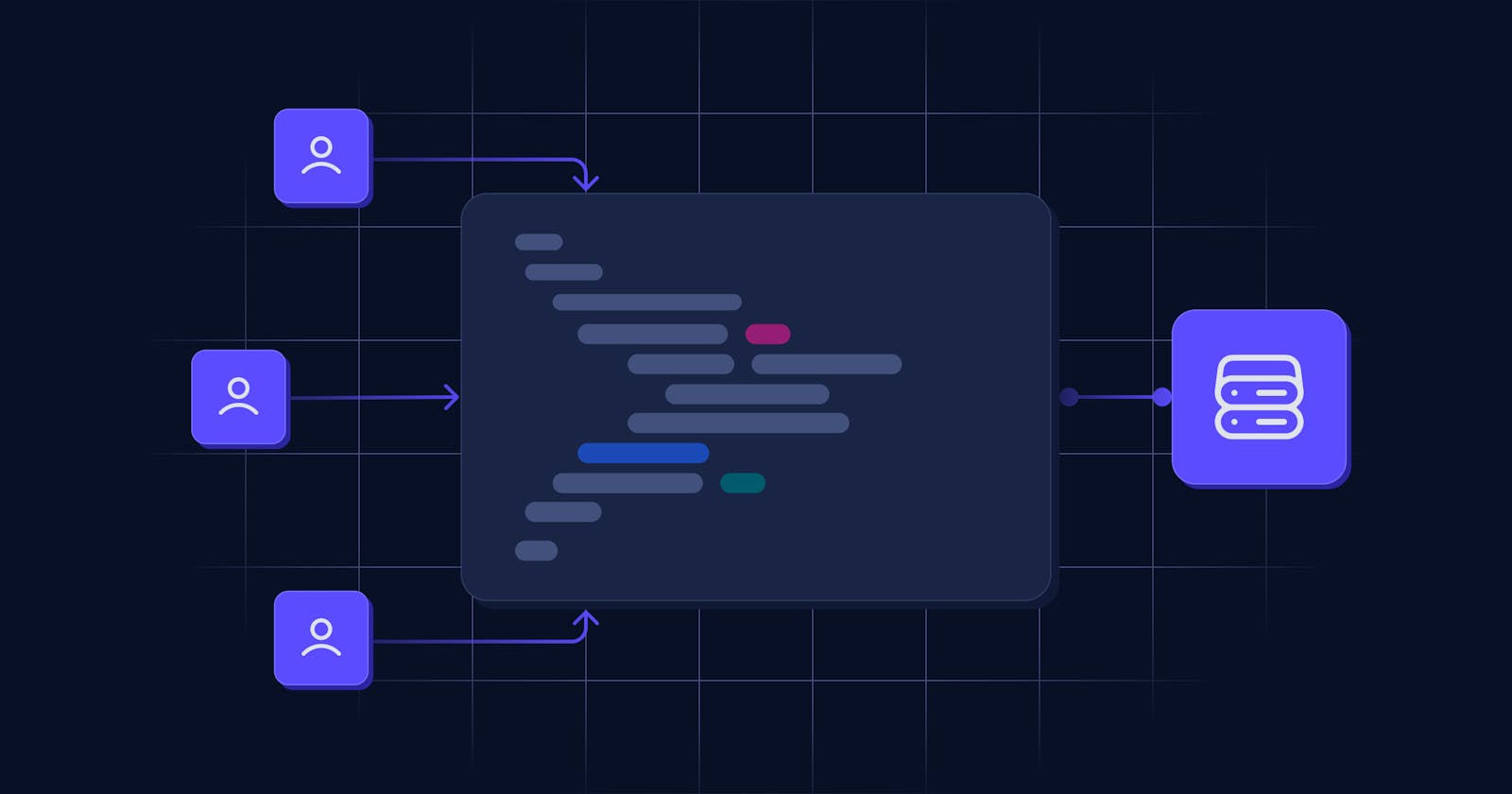
Multi tenancy refers to the concept of multiple users or customers sharing the same resources, such as a software application or a physical infrastructure. Each user or customer is referred to as a tenant and has their own unique set of data and configurations, while still utilizing the same underlying resources.
Advantages of Multi Tenancy
One of the main advantages of multi tenancy is cost efficiency. By sharing resources, the cost of development, maintenance, and infrastructure can be spread across multiple tenants, making it more affordable for each individual tenant. Additionally, multi tenancy allows for easy scalability and flexibility, as new tenants can be added or removed as needed without disrupting the existing infrastructure.
Another advantage of multi tenancy is the ability to provide a customized experience for each tenant. Each tenant can have their own set of data and configurations, allowing them to tailor the application or infrastructure to their specific needs.
Examples of Multi Tenancy
Cloud Computing: One of the most common examples of multi tenancy is in cloud computing. Services such as Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure allow multiple tenants to share the same physical infrastructure, such as servers and storage. Each tenant is given their own virtualized environment, where they can deploy and manage their own applications and data.
Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS applications, such as Salesforce and Office 365, also utilize the concept of multi tenancy. Each tenant has their own unique set of data and configurations, but all tenants are using the same underlying application and infrastructure.
Co-Working Spaces: Even in the physical world, multi tenancy can be found. Co-working spaces, where multiple companies share a single office building, are an example of multi tenancy. Each company has their own designated space, but they all share common areas such as restrooms and break rooms.
Multi Tenancy vs Single Tenancy
It is important to understand the difference between multi tenancy and single tenancy. Single tenancy refers to an environment where each customer or user has their own dedicated resources, such as a dedicated server or application. This means that each customer has their own unique set of data and configurations, and there is no sharing of resources between customers.
While single tenancy offers complete control and customization for each customer, it can also be much more expensive due to the lack of resource sharing. In single tenancy, each customer must pay for their own dedicated resources, even if they are only using a fraction of those resources.
On the other hand, multi tenancy allows for cost efficiency through resource sharing. However, it can also result in lower levels of control and customization for each tenant. It is important for organizations to weigh the trade-offs between multi tenancy and single tenancy, and determine which approach best meets their specific needs.
Challenges of Multi Tenancy
While multi tenancy has many advantages, there are also some challenges that must be addressed. One of the main challenges is ensuring that each tenant's data is secure and protected from other tenants. This requires careful planning and implementation of security measures, such as access controls and data encryption.
Another challenge is ensuring that the underlying resources are allocated and managed in a fair and equitable manner. If one tenant is using a disproportionate amount of resources, it can negatively impact the performance and availability of the resources for other tenants.
Additionally, multi tenancy can also result in a complex administrative and management environment. Service providers must ensure that each tenant is able to configure and customize their environment, while also ensuring that the underlying resources are managed in a consistent and efficient manner.
Conclusion
Multi tenancy is a cost-efficient approach for service providers and tenants, but also requires careful planning and management to ensure that each tenant's data and environment are secure and well-maintained. It is important for organizations to carefully consider the trade-offs between multi tenancy and single tenancy, and determine which approach best meets their specific needs. By understanding the advantages, examples, and challenges of multi tenancy, organizations can make informed decisions about their technology infrastructure and applications.